The way people cultivated, harvested, and accessed food 50 years ago is not the same as today. With the emergence of technologies such as artificial intelligence, blockchain, and the Internet of Things (IoT), a lot has changed regarding how we grow and handle food. In this article, we will take you through how various technology inventions have impacted the food industry in the last couple of years.

We will also look at some of the downsides/threats that need to be addressed if everyone is to fully benefit from the integration of technology in the food growth and supply chain. Without wasting any more of your time, let’s get started right away.


How Technology Impacts The Way We Grow, Trade, and Eat Food
Genetically modified foods


Biotechnology techniques are being used to genetically modify food species to make them grow faster and more resistant to harsh environmental conditions. Foods that are genetically modified are more resistant to pests and herbicides and also have more nutritional value than their original value.
This technology took off when the very first genetically modified tomato was approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the US. This encouraged scientists to research ways of genetically modifying other food species. Today, there are a lot of genetically modified food species, including rice, wheat, and several other grains.
This same technology is also being used to genetically modify poultry and animals to create breeds that grow faster and with more meat. The main benefit of using this technology is the drastic increase in the amount of food produced per acre. This has led to more food supply to feed the world’s ever-growing population.
Personalized Nutrition


Technology advancements have made it much easier for everyday people to personalize their meals. Personalized Nutrition involves eating food based on your DNA. The only challenge in the past was that getting these personalized meals required one to visit the hospital or nutritionists, which are usually very expensive.
Today, we have startups like NGX that develop genetically personalized meal shakes. This company offers affordable at-home DNA nutrition tests and uses the result to personalize meal shakes for every individual. Every individual’s shake comes with the right amount of proteins, carbohydrates, vitamins, and other food nutrients tailored to their body type and DNA.
This reduces the risk of being overweight and getting nutritional-related complications. The good news is that personalized meals created by companies like NGX are affordable for the everyday person. For instance, NGX’s all-in-one personalized meal shakes start from £2.12 per meal.
3D Food Printing

3D Printing is one of the latest inventions in the manufacturing industry that enables production without wasting materials. In the food industry, 3D Printing makes it much easier to personalize food products without having to incur extra costs on tools and machinery. 3D food printers can be used to create food products in various shapes without making any physical changes to the tools and equipment used in the production process.
Changes are only made in the software that determines the shape and the size of the food product to be created. 3D food printers are commonly used to create personalized food like chocolate, cakes, and more. With this technology, it is possible to easily create a piece of cake or chocolate that bears someone’s name.
A lot of research is still ongoing to improve 3D food printing technology with the goal of using it to produce foods at scale. NASA has recently developed a 3D printer that can be used to create Pizza. This could possibly speed up the process of creating Pizza for thousands of people. We expect to see more inventions in the 3D food printing space in the next couple of years.
Food traceability using blockchain technology


Blockchain technology is a pretty recent innovation. However, it has use cases in almost every industry. When it comes to the food industry, this technology is being used to trace the journey of different foods right from the source to production, consumption, and disposal. This makes it easier for customers to know where the food they are eating is coming from.
It is also much easier to identify the responsible parties if certain foods on the market create problems for the consumers. One simply has to scan the code on the food packaging to get all the details about the food’s journey. It should be noted that the information added to the blockchain database cannot be deleted or edited by anyone.
Once an agent in the food supply chain enters information about a particular food product, no one can change it along the way. The main benefit of using this technology to track food is to ensure everyone in the production and the supply chain plays their role to avoid being held accountable if anything goes wrong with the product during its life cycle.
Excess food trading apps


Technology is also being used to reduce the food wasted in the supply chain. A 2020 study by the World Food Program shows that over 1.3 billion tons of food are wasted each year. This wasted food costs approximately $1 Trillion. To help reduce this number, several apps have been developed to help people list and sell excess food in their homes or restaurants at a fraction of the original price.
One of these apps is OLIO, which helps neighbors share excess food with those who need it. OLIO is striving to reduce the over 50% of food wasted in our homes, yet hundreds or thousands of people in our neighborhood might need it. Another example of excess food trading/sharing apps is TOO GOOD TO GO.
TOO GOOD TO GO allows restaurants, cafes and bakeries to list leftover food that would otherwise be thrown away. Users can sign up on the app to browse through restaurants within their neighborhood that might have this excess food that is usually sold at a small fraction of the original cost. If these apps were to be used in every part of the world that has access to the internet, the 1.3 billion tons of food that are wasted would significantly be reduced.
Precision Agriculture


The term precision agriculture refers to the use of information technology (IT) to ensure that crops and soil receive exactly what they need for optimum health and productivity. The objective of precision agriculture is to boost the productivity of farmlands and to ensure the protection and sustainability of the environment.
With precision agriculture, IoT devices are used to gather soil data, including its moisture content and nutrients such as zinc and phosphorus. This data determines the ideal crops to grow in a specific area. Farmers can also use this data to determine the exact amount of nutrients that the soil in their farmland needs to support certain crops.
Ultimately, this eliminates the possibility of using excess agricultural inputs in farmlands that may not necessarily need them. Precision agriculture is mainly used in vertical and indoor farms that primarily rely on automation to supply the required nutrients and water that the crops need to grow.
Restaurant digitization


We have seen a shift to digitizing several restaurant operations with the goal of improving user experience. The covid19 pandemic further escalated the rate at which restaurants adopted digital solutions in most of their operations. Most restaurants now offer online delivery, which allows users to access food menus through an app and order their meals with just a few clicks.
More restaurants have also adopted cashless and handsfree payments enabling users to make payments using platforms such as Apple Pay, Google Pay, PayPal, and more. Using cashless payments makes it easier for restaurants to track their revenue and expenditure. There is no need for manually inputting sales data since it can be automatically imported from these payment platforms.
Restaurants are also adopting the use of chatbots to handle most of the customer support tasks that don’t require human judgment or making decisions that need critical thinking. For instance, if a customer needs to have a look at a menu for drinks, a chatbot can easily share a link to the drink’s menu. These kinds of tasks don’t need to be done by humans.
Drones to monitor farmlands
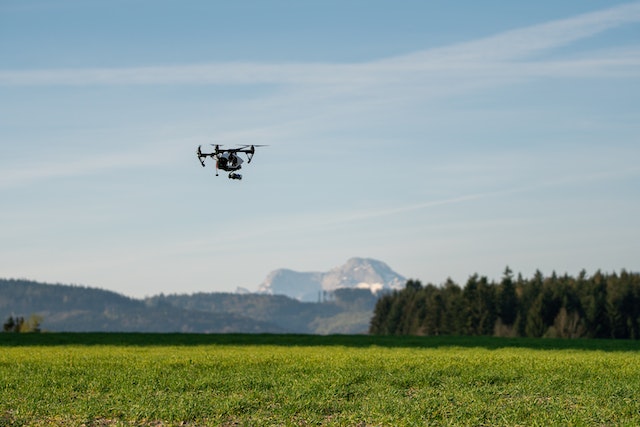


Agricultural entrepreneurs with extremely large farmlands are now using drones to help them monitor the sections of the farm that are too far away. This helps them quickly identify the crops affected by diseases or any other issues that might need their attention. These drones also help to monitor the progress of the different crops in the garden to determine when to do certain farm activities, such as weeding, pruning, and harvesting.
Besides monitoring crops, drones are also crucial in ensuring the farm is secure. Most farmers are continuing to adopt the use of drones as their prices are constantly dropping year over year. Using drones also eliminates the need for full-time workers to do these monitoring tasks. You only need a few skilled people that can control the movement of drones and interpret the information captured in the footage.
Threats that arise from the use of technology in the food industry
Concerns about the risk of Genetically modified foods


Despite being approved by legitimate authorities such as the FDA in the US, people are still concerned about the long-term effect of genetically modified foods. There is research suggesting that some GMO plants might have a different balance of toxins, increasing the risk of harm to humans. This kind of data prohibits so many people from trusting these foods.
Addressing such concerns might take time as research must be done after these foods have been used for longer periods. Remember, the creation of genetically modified was widely adopted in the late 1990s. So, most of the GM foods in the market are less than 20 years old.
The cost of adopting some technologies is still high.


The price of buying equipment and tools to utilize inventions such as precision agriculture or 3D food printing is still high. Several small businesses in the food sector still use traditional methods in their operations mainly because they cannot afford the tools and equipment required to leverage the benefits of these technologies.
This problem will still exist until the price of these cutting-edge technologies drops to the point where every person running a small business doesn’t feel it.
Privacy concerns


Using services such as ordering food online exposes some of our personal information to the companies running these platforms. For instance, most food delivery services will need your email address, phone number, and location before processing your food order. We now also have companies that offer personalized meals after testing your DNA.
This simply means your DNA information is in the hands of a small startup that may not necessarily follow the guidelines for handling such information. People who are sensitive about their privacy may not be okay with using these services. It also requires stakeholders in the food industry to be transparent regarding the data they need from us and how they intend to use it.
Final thoughts


Overall, technology has played an enormous role in advancing the food industry in the last couple of years. Many individuals are now utilizing the recent innovations in the food industry to improve their food habits or at least reduce the costs they spend on food. Small businesses are also leveraging these technologies to reach more customers and reduce overall operational costs.



